Git basics
Grzegorz Kowzan
1. Git basics
1.1. Why use version control
- remember all old versions of code, manuscript, notes
- annotate changes, same way you annotate work in you lab notebook
- keep track of code authorship
- facilitate collaboration
- work on multiple versions of the same code without getting lost
1.2. What do we want from a version control system?
- save the current state of a directory structure - a commit
/Users/gkowzan/d/python/packages/kogelnik:
drwxr-xr-x 3 gkowzan staff 96 2023-06-02 docs
drwxr-xr-x 24 gkowzan staff 768 2023-06-02 examples
drwxr-xr-x 22 gkowzan staff 704 2024-11-08 kogelnik
drwxr-xr-x 7 gkowzan staff 224 2023-06-02 refractivesqlite
-rw-r--r-- 1 gkowzan staff 17K 2022-04-08 MainWindow.py
-rw-r--r-- 1 gkowzan staff 20K 2022-04-08 MainWindow.ui
-rw-r--r-- 1 gkowzan staff 149 2022-04-08 Makefile
-rw-r--r-- 1 gkowzan staff 1,4K 2022-04-08 MatplotlibWidget.py
-rw-r--r-- 1 gkowzan staff 1,3K 2022-04-08 VerticalScrollArea.py
-rw-r--r-- 1 gkowzan staff 20K 2023-11-09 main.py
-rw-r--r-- 1 gkowzan staff 948 2022-04-26 materials.py
-rw-r--r-- 1 gkowzan staff 6,6K 2024-11-08 nlo.py
-rw-r--r-- 1 gkowzan staff 17K 2024-03-12 optics.py
-rw-r--r-- 1 gkowzan staff 22 2022-04-26 __init__.py
-rw-r--r-- 1 gkowzan staff 701 2023-11-09 README.md
-rw-r--r-- 1 gkowzan staff 120 2024-11-08 pyproject.toml
-rw-r--r-- 1 gkowzan staff 1,8K 2024-11-08 requirements.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 gkowzan staff 875 2024-11-08 setup.cfg
- track datetime, author and other metadata, e.g. comments, on the current state of the directory structure - commit metadata
commit 68263f7f39dd7b7611da4beaaaa80aef4039e7d2 (HEAD -> master, lsuu/master)
Author: Grzegorz Kowzan <gkowzan@umk.pl>
Date: Wed Jan 10 13:22:37 2024 +0100
fix references to np.complex
kogelnik/optics.py | 2 +-
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+), 1 deletion(-)
- specify parent-child relation between commits, focus only on the changes between them
diff --git a/setup.cfg b/setup.cfg
index 6275d00..e5340f9 100644
--- a/setup.cfg
+++ b/setup.cfg
@@ -24,10 +24,12 @@ install_requires =
appdirs
sympy
PyYAML
+ Cython < 3.0
xarray
PyQt5
sip
requests
+ attrs
[options.entry_points]
console_scripts =
- split development into independent tracks and provide ways to merge them
* fe73c2a Merge remote-tracking branch 'allisonlab/master'
|\
| * a56bf72 Add README.md
* | 5ef9fd7 fixed setup.py
|/
* d96eb8d added egg info
* 4ac0c38 initial commit
1.3. Design of Git
Git saves snapshots of file structure
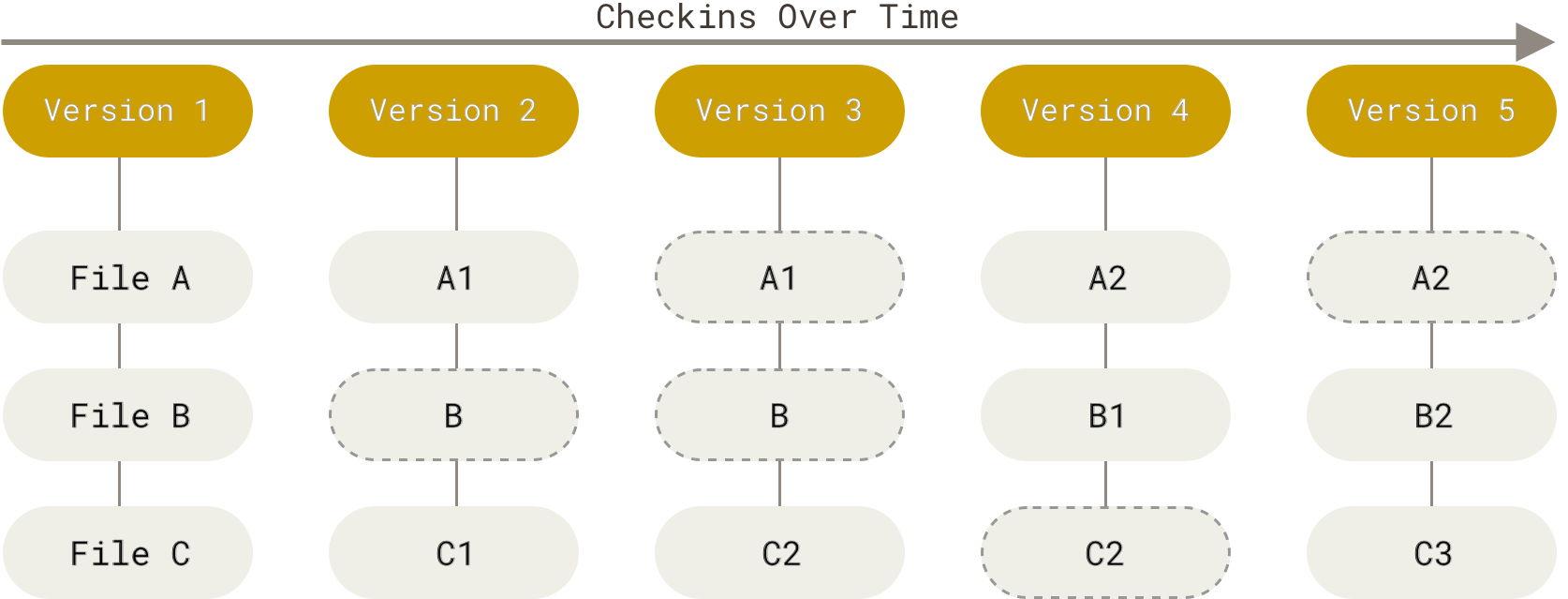
Git can be used completely locally, you can copy your repository to a remote location and consider it the central repository but you don't have to
Every object git records is checksummed and has a unique id. Any data corruption or loss is easily detected.
As long as you commit changes, you will be able to retrieve them later. You have to try to erase any data.
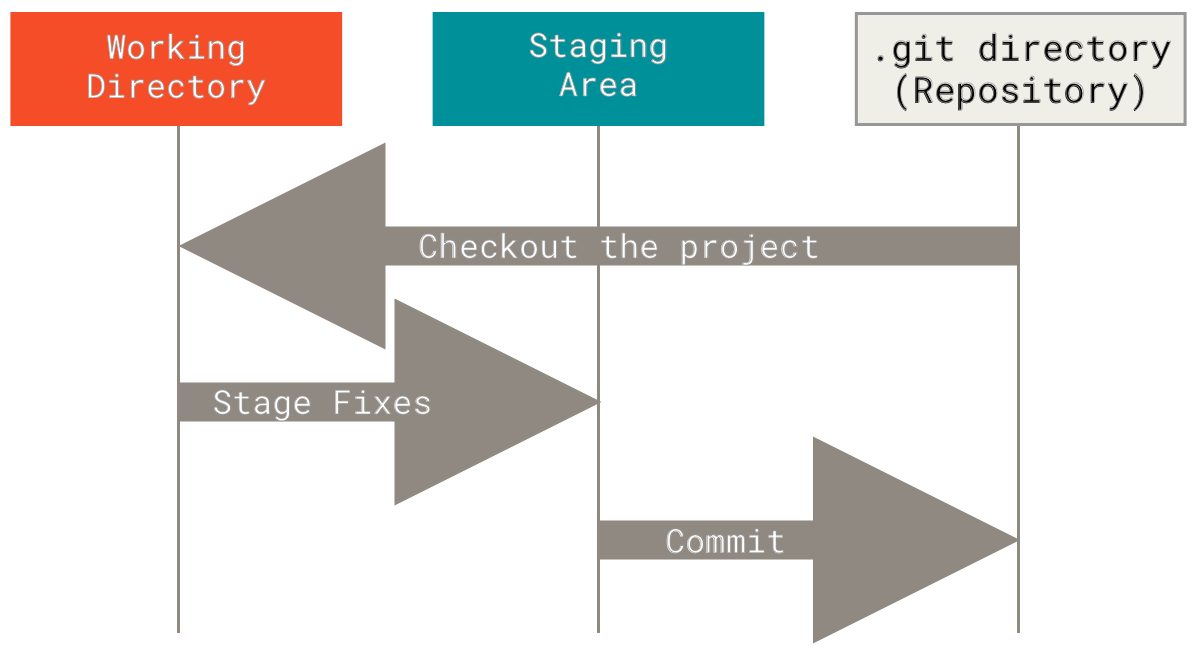
1.4. Three states of Git
- working directory - current state of files on your disk
- staging area (index) - a temporary snapshot that may be committed to permanent storage
- commit history - the snapshots which were committed to permanent storage
1.5. More git details
Git is a content-addressable filesystem, which means that Git is a key-value data store (like Python dictionary), where keys are the SHA hases.
In principle, you can use git as a database and ignore all version control features.
All the data is stored in .git/objects directory.
Store some blob:
find .git/objects
echo 'test content' | git hash-object -w --stdin
find .git/objects -type f
git cat-file -p d670460b4b4aece5915caf5c68d12f560a9fe3e4
echo 'version 1' > test.txt
git hash-object -w test.txt
git cat-file -t 1f7a7a472abf3dd9643fd615f6da379c4acb3e3a
We also have tree objects:
$ git cat-file -p master^{tree}
100644 blob a906cb2a4a904a152e80877d4088654daad0c859 README
100644 blob 8f94139338f9404f26296befa88755fc2598c289 Rakefile
040000 tree 99f1a6d12cb4b6f19c8655fca46c3ecf317074e0 lib
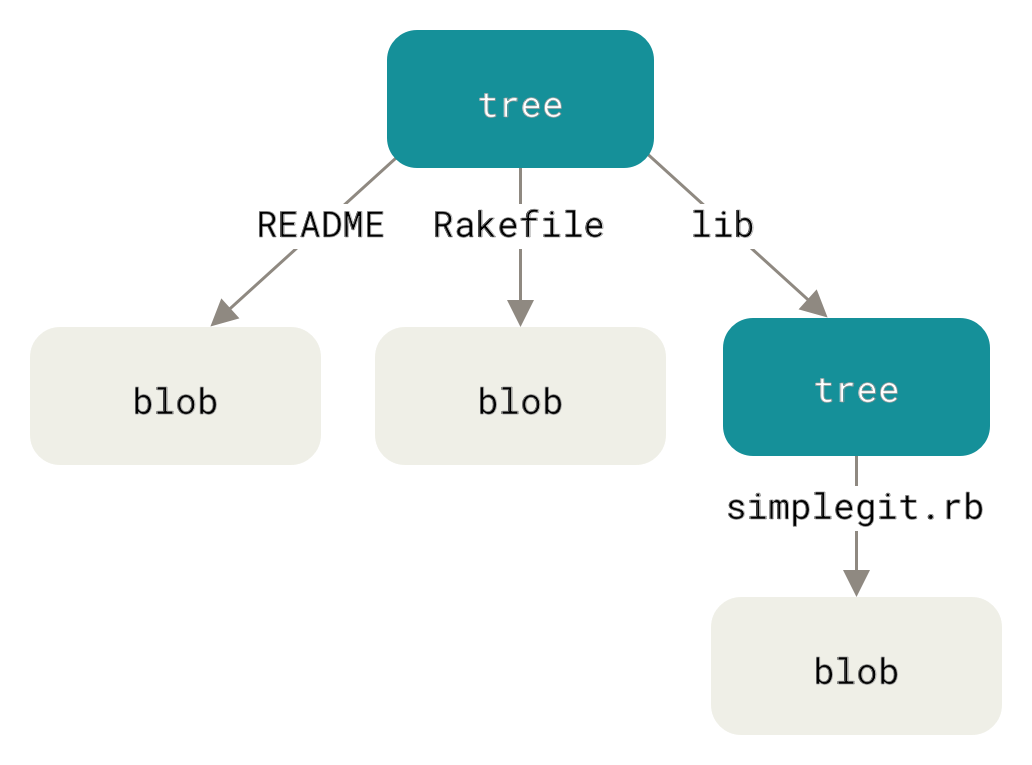
The tree object and each blob has a checksum identifier. This is how git records snapshots of the working tree.
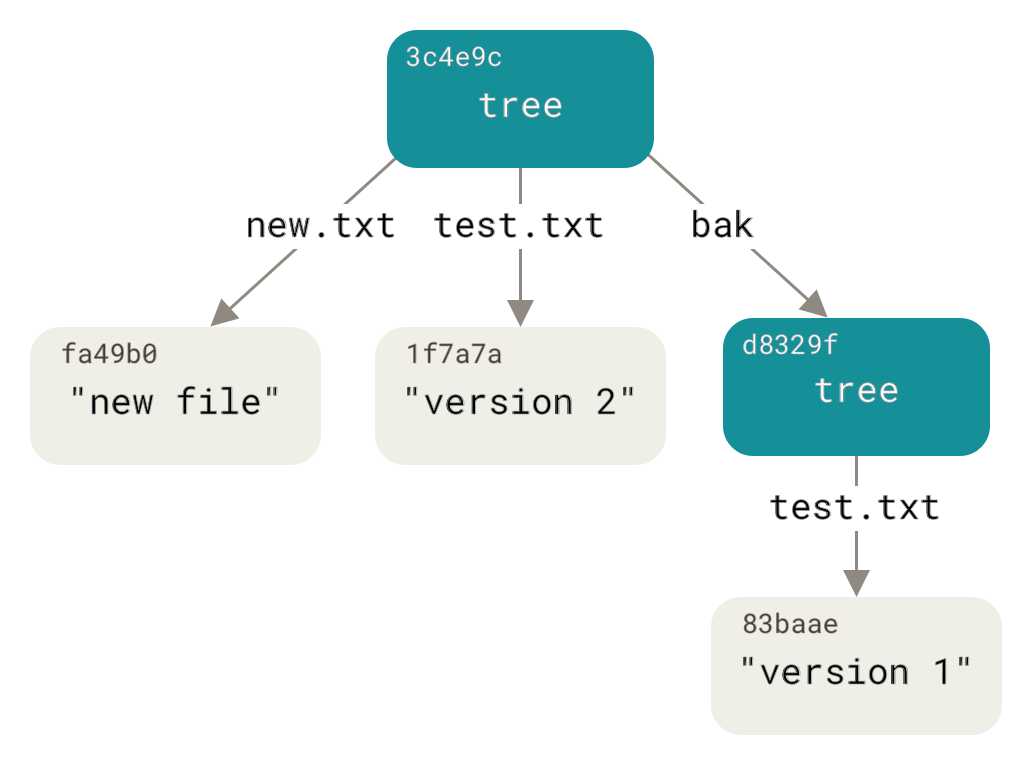
Now we just need commit objects to obtain all core features of git. Commit object contains this information:
- hash of top-level tree of the commit
- hash of parent commit (if any)
- author information
- commit message
All blobs, trees and commit objects are files in .git/objects directory. Now we have almost all key git repository ingredients.
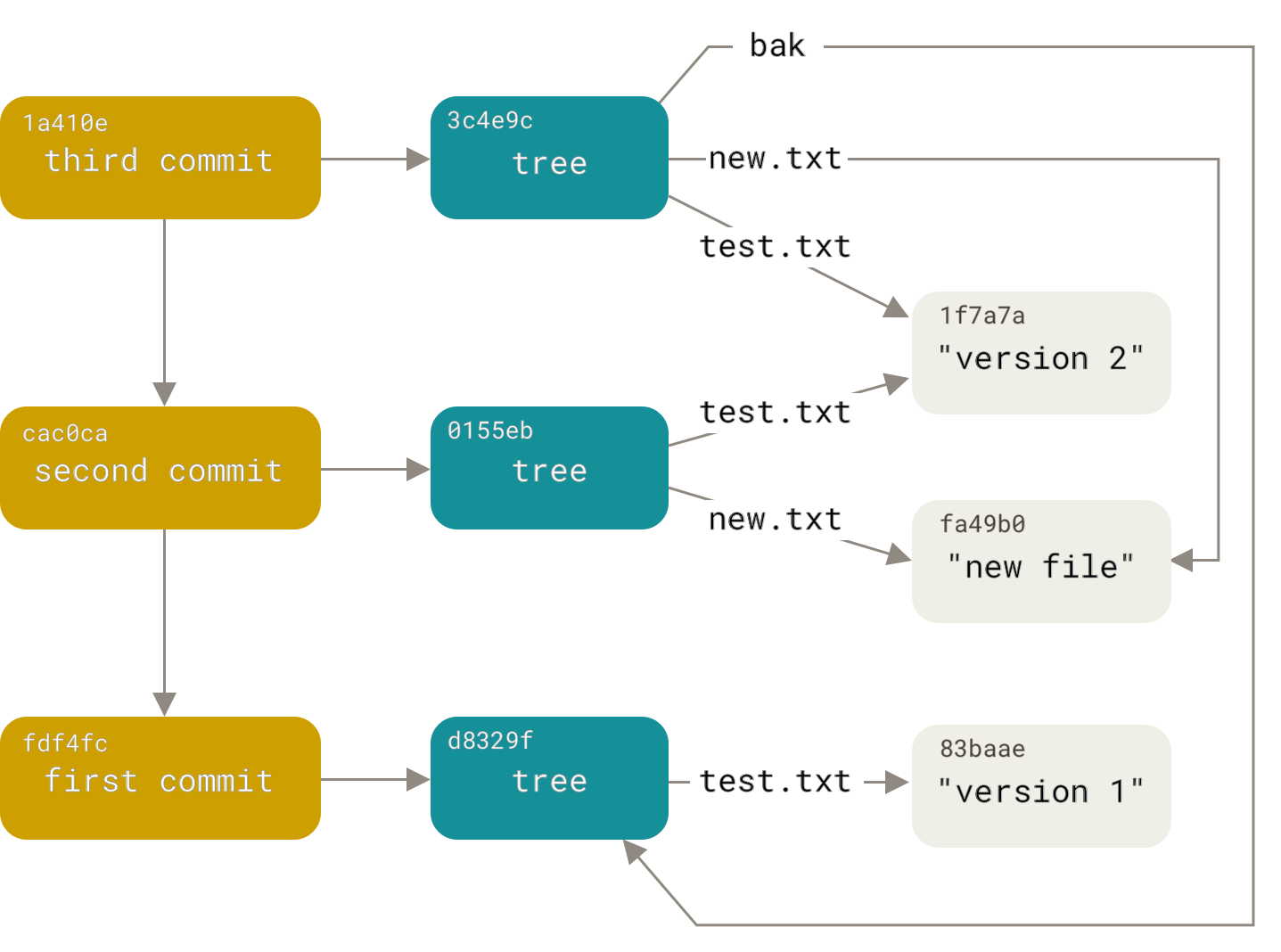
Git also has references, which are aliases/symbolic names for git commits, so we can use names such as master/main, bugfix, feature instead of 99f1a6d12cb4b6f19c8655fca46c3ecf317074e0.
They are stored in .git/refs/.
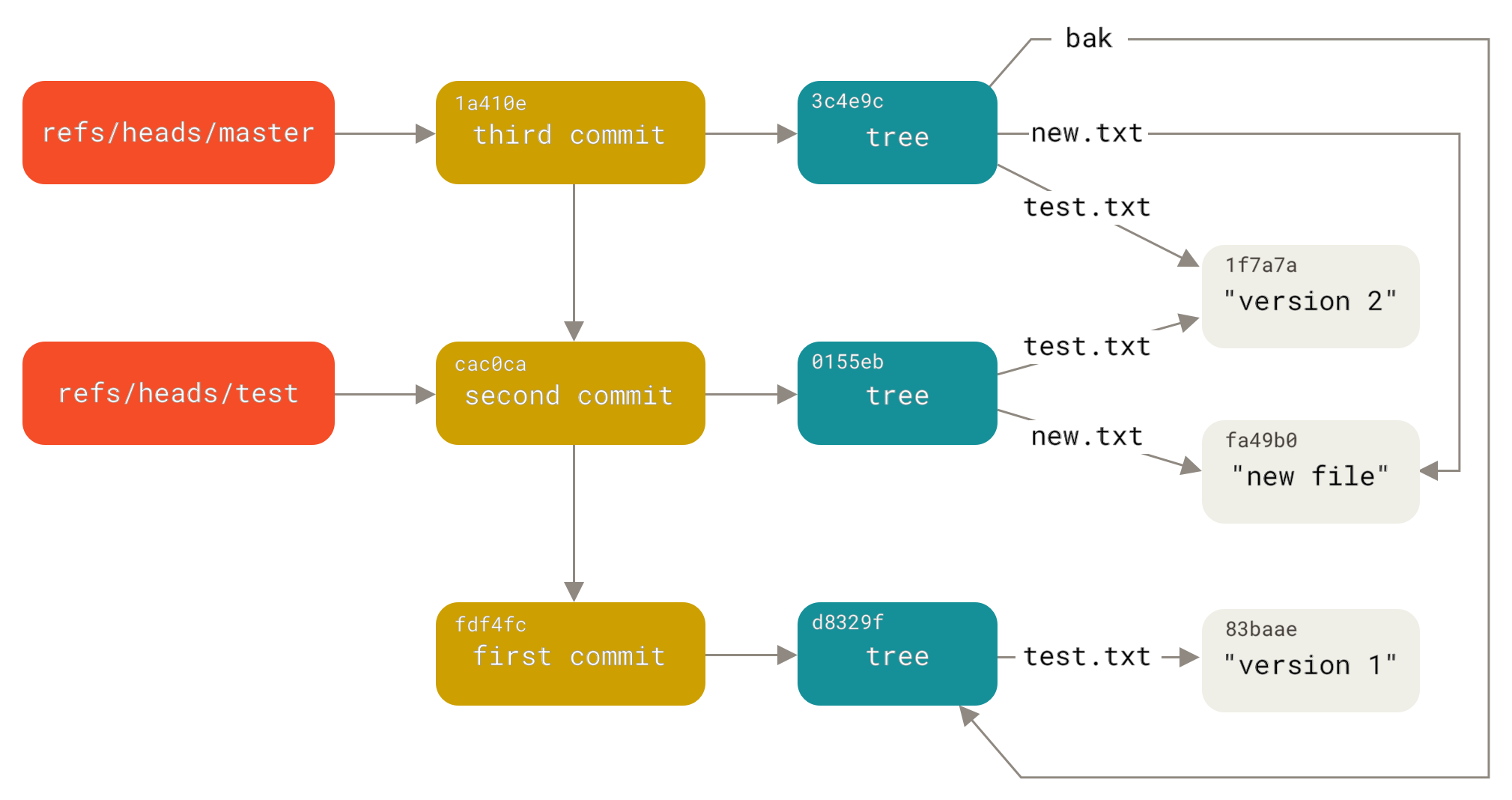
There is a special reference called HEAD, which points to another reference, the branch you are currently on.
If it points to a specific commit, then you have a scary sounding detached HEAD, which does not track any branch.
1.6. Installing git
Lab computers already have git installed, you can use it from Anaconda command prompt.
To install Git on your computer:
- Linux - use your package manager
- Windows - download and install Git for Windows (https://gitforwindows.org/)
- Mac OS - install homebrew, then install git (https://brew.sh/)
Ask for help if you fail.
1.7. Basic git configuration
Set up your full name and email:
git config --global user.name "First Last"
git config --global user.email "name@domain.eu"
On Windows:
git config --global core.autocrlf true
On Linux or Mac OS:
git config --global core.autocrlf input
1.8. Create a repository
- Create new repository, discuss
git status. - Create hello world example, stage, status, commit, status again.
- Show git log, –stat, –oneline.
- Extend
hello_worldto ask for name. - Show status, show git diff, stage, show git diff –cached.
- First line of commit <50 characters.
Exercise 1:
- Modify
hello_world.pyto also print current date and time. - Make new file
fib.pywith functionfibonacci(n)calculating n'th Fibonnaci number. - Run git diff to check differences, stage and commit these changes.
Exercise 2:
- Make new git repository in a directory
bio. - Write a three-line biography of yourself in a file
me.txt, commit changes. - Modify a line and add fourth line.
- Show the diff and commit changes.
1.9. Exploring history
- Show git diff with HEAD~1, HEAD~2 and proper commit hashes. Limit to specific file.
- Use
git showfor commit message and diff. - Use
git-restoreto restore oldhello_world.pyand then un-restore. - Use
git-restore --stagedto stage yet another version. Talk aboutgit diffagain. Undo all. - Use
git showto check out a file under a different name.
Exercise 1:
- Clone rotsim2d repository:
git clone git@github.com:gkowzan/rotsim2d.git. - Restore
setup.cfgto the previous version: usegit logto find commit hash, usegit restoreto bring it back. - Use
git showto see what other changes were made in the same commit.
Exercise 1:
- Use the same rotsim2d repository. Save the first ever version of file
rotsim2d/dressedleaf.pyto fileinitial_dressedleaf.py.
1.10. Branching and merging
Create a new branch:
git branch testing
Switch to a branch:
git checkout testing
See where you are with git log --oneline --decorate or git branch -v.
Make a change that does not conflict with main. Check results with git log --oneline --decorate --graph --all. Fast-forward merge.
Make conflicting changes. Show log and diff between branches. Try to merge. Use git restore to play around with changes.
Exercise 1: Create factorial branch. Add file fac.py with function factorial(n) which calculates factorial of the argument. Switch back to main branch and do fast-forward merge.
Exercise 2: Switch to factorial again. Add __main__ section for testing and add conflicting section in main branch. Perform a merge. Use git branch -d <branch> to delete the factorial branch.
1.11. Simple rebase
Previously we reconciled different branches by performing a merge commit.
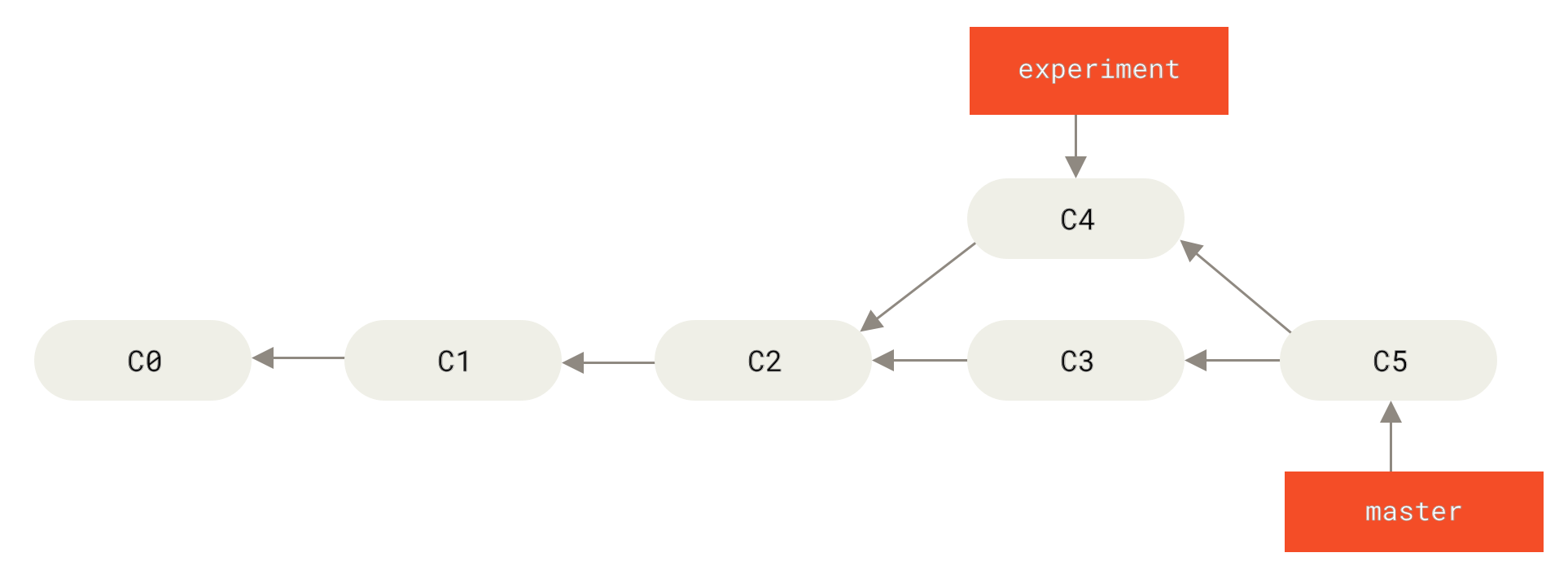
Instead we can take the patch of the change that was introduced in C4 and reapply it on top of C3. This is called rebasing. We rewrite history to make it look nice and linear.
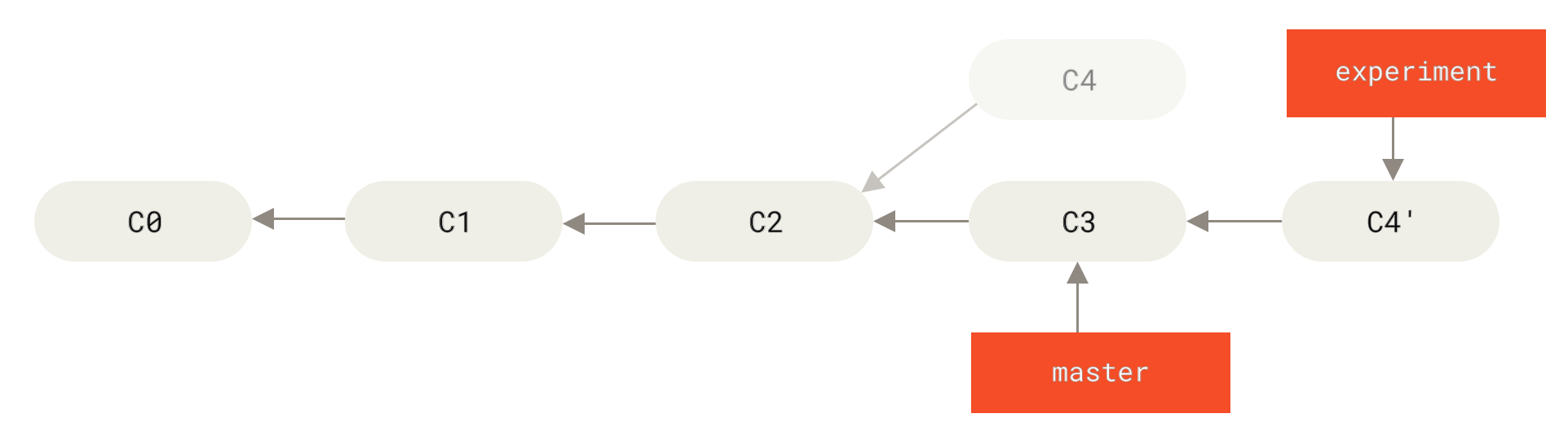
- make file dummy1.txt in one branch and dummy2.txt in another branch, commit them.
- go to dummy branch and do the rebase.
- do fast-forward merge
Why would you do this? You have feature branch that you have been developing for a while, but it is now lagging behind the main branch. Maybe you want feature branch to use new main branch functionality or you just want to make sure your new feature integrates well with the main branch, so you rebase it periodically onto main branch and continue working.
Exercise 1: Make a new branch power and write function power in file power.py calculating integer power of a number. Commit the function. Add __main__ fragment in another commit. Switch to main branch and add function sqrt in file heron.py implementing Heron's algorithm for calculating square root. Rebase power branch onto main branch and fast-forward the main branch.
1.12. gitignore
You usually don't want to track files which are temporary or represent intermediate results. You also don't want them to show up in git status and produce clutter. We can add .gitignore file and tell git to ignore some files.
1.13. Suspending current work
You are working on a new feature but in the meantime you need to fix a bug in the old version of your code.
You're not finished, your code is in shambles and you don't want to commit it, but your working tree is dirty so you can't checkout different branch.
What to do? Use git stash to save the current state in a temporary commit.
1.14. Splitting changes into multiple commits
You made many independent changes to the same file and did not commit any of them.
Doing git add <file> will stage all of them.
Can you split them into separate commits? Yes! Use git add --patch <file>.
Download couple.py, commit it, remove some functions and split the commits.
Exercise 1: Do the same with another file.
2. Git resources
2.1. Git resources
- Version Control with Git - https://swcarpentry.github.io/git-novice/index.html (resource for novices)
- Pro Git book - https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2 (full course, good reference)
- git manpages - https://git-scm.com/docs
- Unix Shell - https://swcarpentry.github.io/shell-novice/index.html (resource for novices)